In Bash shell scripting, you can easily check whether a directory exists or not using various techniques.
Using the '-d' Test Operator
The '-d' Test Operator
The '-d' test operator is used in Bash to check if a directory exists.
Syntax
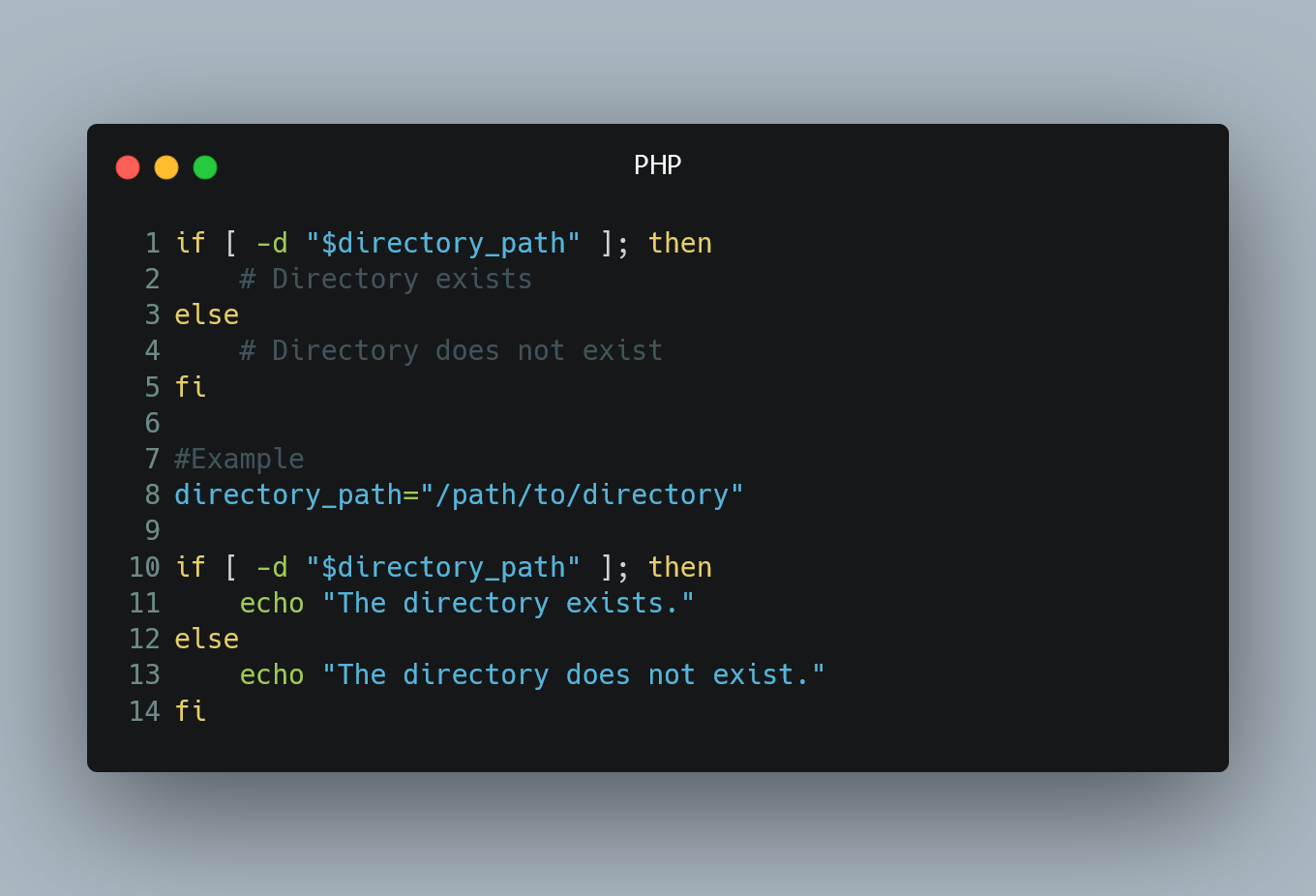
if [ -d "$directory_path" ]; then
# Directory exists
else
# Directory does not exist
fi
Example
directory_path="/path/to/directory"
if [ -d "$directory_path" ]; then
echo "The directory exists."
else
echo "The directory does not exist."
fi
In this example, the '-d' test operator is used to check if the directory specified by the '$directory_path' variable exists. The script prints the appropriate message based on the result of the check.
Using the 'test' Command
The 'test' Command
The 'test' command, also represented by '[ ]', is used for various tests in Bash, including checking for the existence of a directory.
Syntax
if test -d "$directory_path"; then
# Directory exists
else
# Directory does not exist
fi
Example
directory_path="/path/to/directory"
if test -d "$directory_path"; then
echo "The directory exists."
else
echo "The directory does not exist."
fi
In this example, the 'test' command is used with the '-d' option to check if the directory specified by the '$directory_path' variable exists.
Using the '[[ ]]' Construct
The '[[ ]]' Construct
The '[[ ]]' construct is an extended version of the 'test' command and is available in most modern shells.
Syntax
if [[ -d "$directory_path" ]]; then
# Directory exists
else
# Directory does not exist
fi
Example
directory_path="/path/to/directory"
if [[ -d "$directory_path" ]]; then
echo "The directory exists."
else
echo "The directory does not exist."
fi
In this example, the '[[ ]]' construct is used with the '-d' option to check if the directory specified by the '$directory_path' variable exists.
1 Comment


Hello dear can we friends s