In PostgreSQL, you can retrieve information about a table's structure and properties using the "DESCRIBE TABLE" command. This command provides valuable insights into the table's columns, data types, constraints, and more.
Syntax
The syntax for describing a table in PostgreSQL is as follows:
\d table_name
Replace table_name with the name of the table you want to describe. Remember that the table name is case-sensitive.
Describing a Table
To describe a table in PostgreSQL, follow these steps:
# Step 1: Connect to the Database
Before describing a table, make sure you are connected to the PostgreSQL database where the table is located. You can use the psql command-line tool or connect through a graphical client like pgAdmin.
# Step 2: Access the Command Prompt
Once you are connected to the database, access the command prompt or query editor. This is where you will enter the "DESCRIBE TABLE" command.
# Step 3: Use "DESCRIBE TABLE"
Now, enter the following command to describe the table:
\d table_name
Replace table_name with the name of the table you want to describe.
# Step 4: View Table Information
After executing the command, PostgreSQL will display detailed information about the specified table. This information typically includes:
- Column names
- Data types of each column
- Constraints (e.g., primary key, unique, foreign key)
- Default values (if any)
- Nullable columns
Example
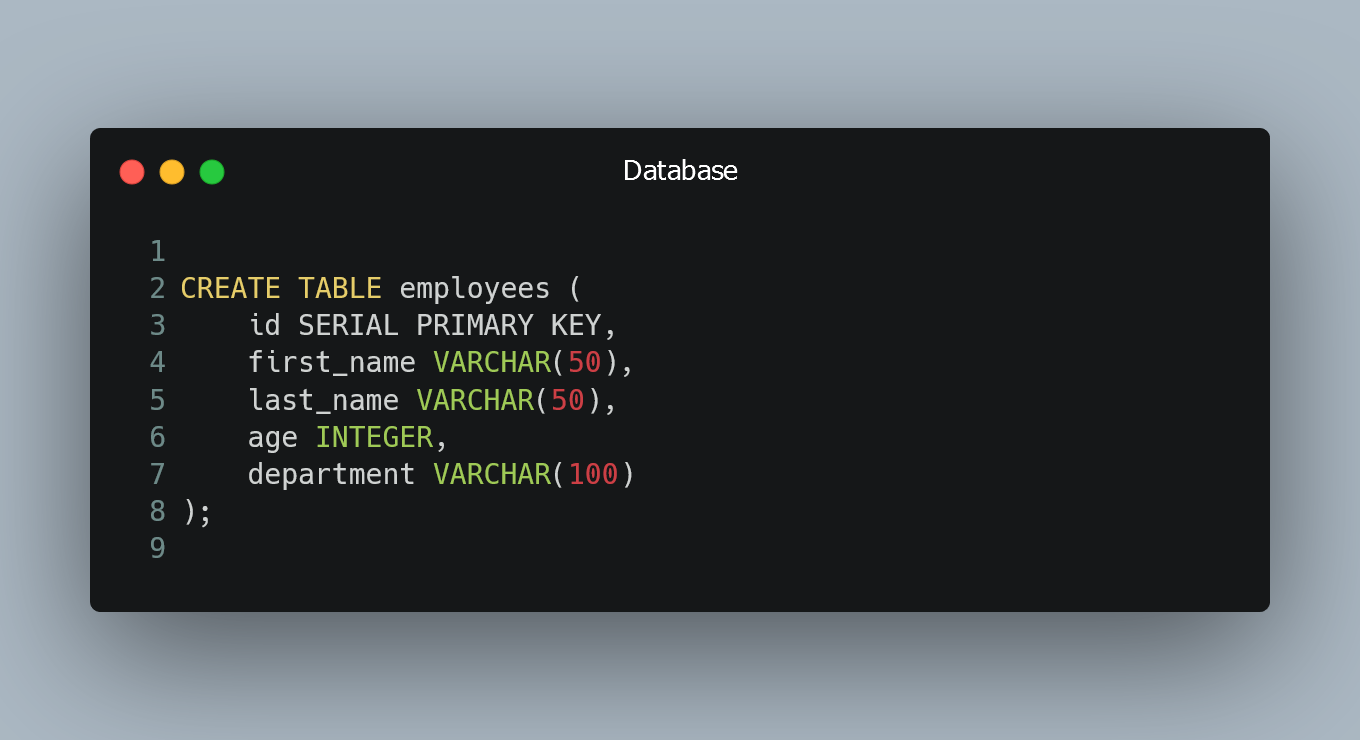
Let's say we have a table named "employees" with the following structure:
CREATE TABLE employees (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
first_name VARCHAR(50),
last_name VARCHAR(50),
age INTEGER,
department VARCHAR(100)
);
To describe this "employees" table, we would run the following command:
\d employees
PostgreSQL would then display information about the table's columns, data types, constraints, and other relevant details.
0 Comment

