To access a Docker container's shell, you can use the docker exec command, which allows you to run commands inside a running container.
Using docker exec command
The docker exec command allows you to execute commands inside a running container, including accessing its shell.
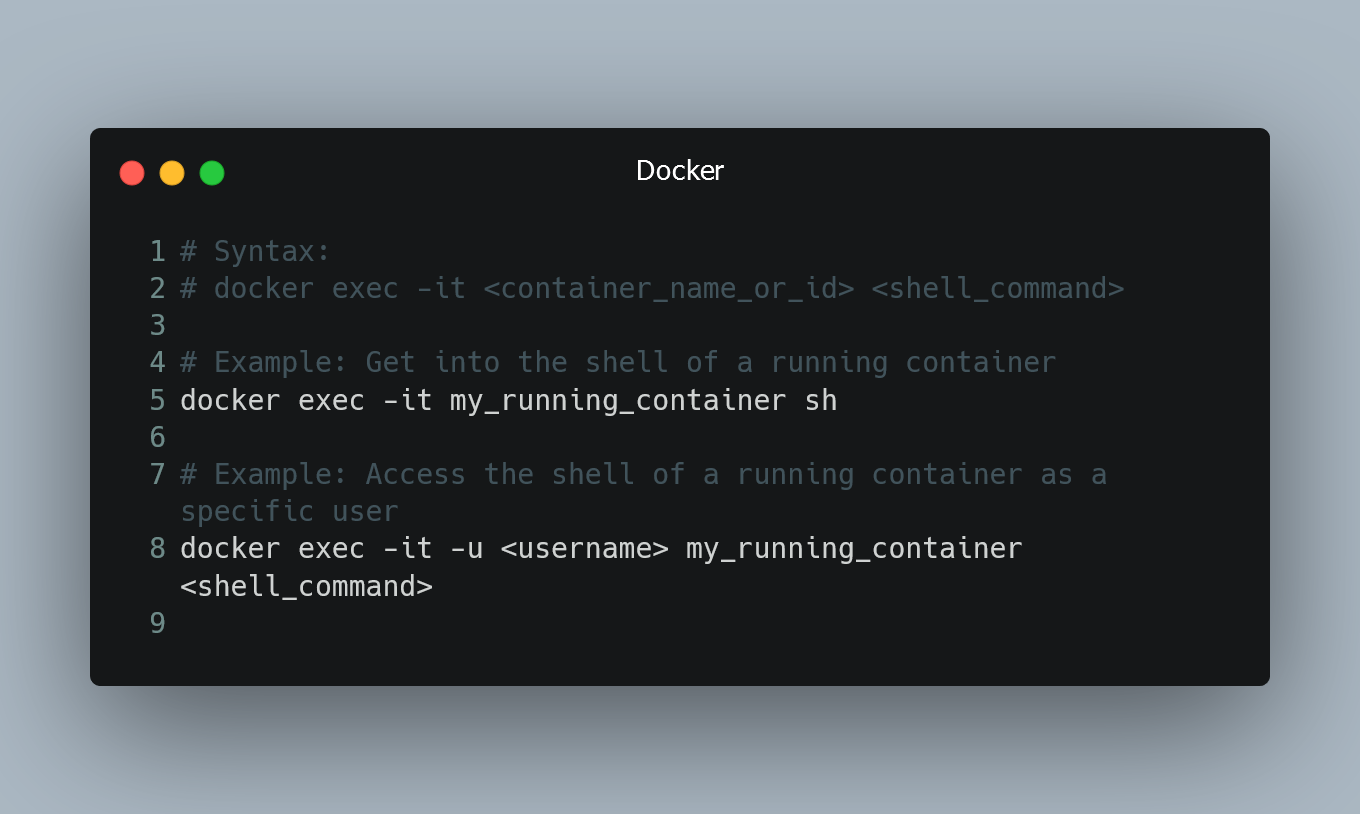
# Syntax:
# docker exec -it <container_name_or_id> <shell_command>
# Example: Get into the shell of a running container
docker exec -it my_running_container sh
Replace <container_name_or_id> with the name or ID of the container you want to access. The -it flags stand for interactive and allocate a pseudo-TTY, allowing you to interact with the container's shell. After the flags, specify the shell you want to use (e.g., sh, bash, zsh, etc.).
Example: Accessing a specific user's shell
You can also specify a particular user's shell inside the container.
# Example: Access the shell of a running container as a specific user
docker exec -it -u <username> my_running_container <shell_command>
Replace <username> with the desired username, and <shell_command> with the shell you want to use (e.g., sh, bash, zsh, etc.).
Example: Using docker-compose
If you are using docker-compose, you can access the container's shell with the following command:
# Example: Get into the shell of a running container using docker-compose
docker-compose exec <service_name> <shell_command>
Replace <service_name> with the name of the service defined in your docker-compose.yml file, and <shell_command> with the shell you want to use (e.g., sh, bash, zsh, etc.).
0 Comment

